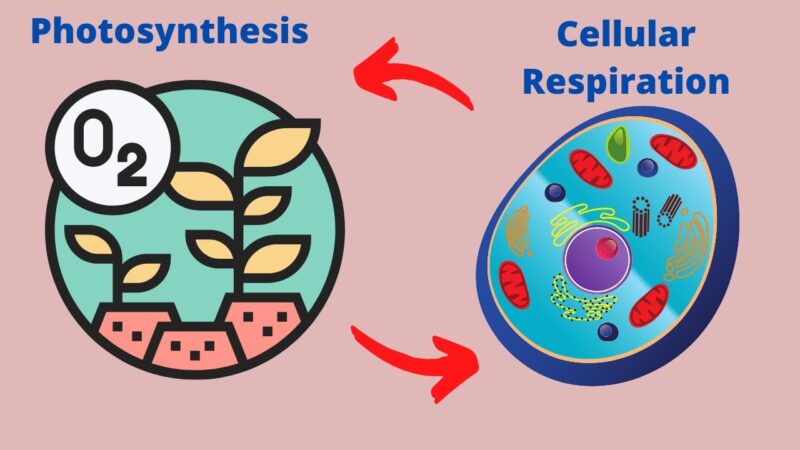
Have you ever stopped to think about the intricate processes that keep our world alive and thriving? Two of the most vital processes in the biological realm are photosynthesis and cellular respiration. These processes are like two sides of the same coin, each playing a pivotal role in sustaining life on our planet.
Photosynthesis, in a nutshell, is the magical process where plants, algae, and some bacteria transform sunlight into energy. Imagine the sun’s rays being captured and converted into food for these organisms.
Cellular respiration is the process where all living cells, including those in plants and animals, release the energy stored in food. It’s like the cells’ way of “eating” and “breathing.”
Now, here’s the fascinating part: these two processes are deeply interconnected. While photosynthesis produces oxygen and stores energy, cellular respiration uses that oxygen to release stored energy. It’s a beautiful symbiotic relationship, with each process complementing the other. Think of it as nature’s perfect give-and-take system.
Photosynthesis: The Green Factory
You know, every time I step outside and feel the warmth of the sun on my skin, I’m reminded of the incredible process of photosynthesis. It’s like nature’s very own solar panel system. In simple terms, it is that magical process where plants and some microorganisms take in sunlight and convert it into energy.
Imagine if we could do that. Breakfast would be a morning sunbath! But jokes aside, this process is the reason we have food on our table and oxygen to breathe. Plants use this energy to create sugars, which they store for later or use right away.
| Fact | Description |
| Primary Function | Conversion of light energy into chemical energy |
| Main Players | Chloroplasts and Chlorophyll |
| Key Ingredients | Sunlight, Carbon Dioxide, and Water |
| Byproducts | Oxygen and Sugars |
The Role of Chloroplasts
Now, let’s talk about the real MVPs of photosynthesis: chloroplasts. These tiny green structures inside plant cells are like mini-factories. They’re packed with a pigment called chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color. But more importantly, chlorophyll captures sunlight and starts the whole energy conversion process. It’s like the engine room of a ship, driving the entire operation.
The Key Ingredients of Photosynthesis:

- Sunlight: Capturing energy – Sunlight is the primary source of energy for photosynthesis. Plants have these amazing molecules that capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. It’s like they have millions of tiny solar panels on their leaves!
- Carbon Dioxide: The carbon source – Plants are great listeners. They take in carbon dioxide from the air, which we and other animals exhale. This CO2 is a key ingredient they use to make sugars. It’s a beautiful cycle, isn’t it?
- Water: The source of electrons – Water is essential for life, and it plays a crucial role in photosynthesis too. Plants take up water from the soil, and during photosynthesis, they split it to release oxygen (which we breathe in) and use the electrons to generate energy.
Alright, for those of you who love a good equation, here it is:
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Now, to get a bit technical. During photosynthesis, the energy from sunlight is stored in two molecules: ATP and NADPH. Think of them as the batteries of the cell. They store energy and then release it when the plant needs it. It’s like having a backup generator for when the power goes out.
Cellular Respiration: The Energy Release
The other side of the coin is when we talk about photosynthesis. While plants are busy capturing sunlight and converting it into energy, our cells are hard at work releasing that energy and making it usable for our daily activities. Let’s get into the details.
Cellular respiration, in a nutshell, is the process by which cells in our bodies convert the energy stored in the chemical bonds of food molecules into a form that the cell can use, namely ATP. It’s happening right now in every cell of your body. Think of it as your cellular power plants working 24/7 to keep you moving, thinking, and even sleeping.
The Role of Mitochondria
Now, where does all this magic happen? Enter the mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell. These tiny organelles are where most of the cellular respiration processes occur. They’re like the engines of our cells, burning fuel (in the form of glucose) and releasing energy.
Key Stages:
- Glycolysis: Right off the bat, glucose, a simple sugar, undergoes a process called glycolysis. This happens in the cytoplasm of our cells and results in the production of pyruvate. It’s like the first step in breaking down the energy-packed glucose molecule.
- Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle): The pyruvate then enters the mitochondria and gets further broken down in the citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle. Here, more energy is extracted, and we get some important molecules like NADH and FADH2, which will play a crucial role in our next step.
- Electron Transport Chain: This is where the real action happens. The NADH and FADH2 produced earlier donate their electrons to a series of proteins in the inner mitochondrial membrane. This flow of electrons, coupled with the pumping of protons, creates a gradient. At the end of this chain, the electrons combine with oxygen (yes, the one we breathe in) to form water. The energy from this process is used to produce a significant amount of ATP.
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 -> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP
The end goal of cellular respiration is to produce ATP, the energy currency of our cells. ATP is generated in two main ways during this process: substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation. The former produces ATP directly in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, while the latter, which happens in the electron transport chain, produces the bulk of the ATP.
The Interplay Between Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
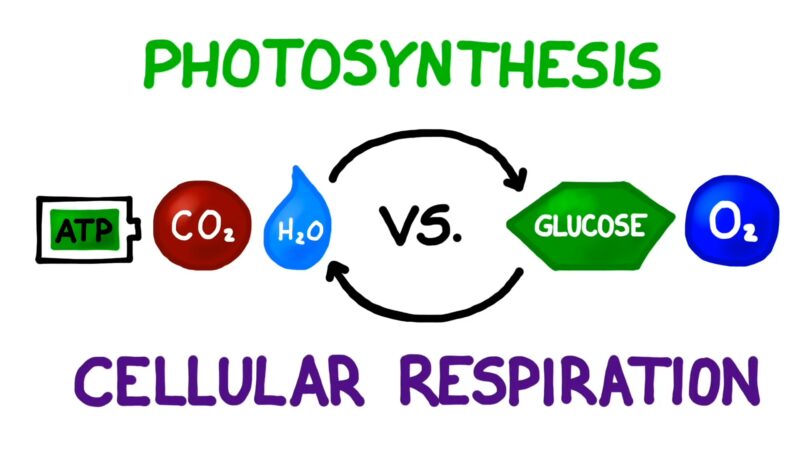
Isn’t it fascinating how nature has its way of balancing things out? Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are like two dancers in a perfectly choreographed ballet, each relying on the other to maintain the rhythm of life.
Energy Flow
Let’s start with the energy flow. Photosynthesis captures sunlight and converts it into chemical energy stored in glucose. This glucose then becomes the primary fuel for cellular respiration in plants, animals, and other organisms. In a way, photosynthesis charges the battery, and cellular respiration uses that charge. It’s a continuous cycle of energy capture, storage, and release.
Exchange of Gases
Now, let’s talk about breathing. Plants take in carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and release oxygen as a byproduct. We, and other animals, do the exact opposite during cellular respiration. We consume oxygen to break down glucose and release carbon dioxide. It’s like a beautiful exchange program where everyone benefits.
Symbiotic Relationship
The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is truly symbiotic. Plants provide animals with oxygen and food, and in return, animals provide plants with carbon dioxide and, in some cases, nutrients from their waste. This interconnectedness ensures that life on Earth thrives and that energy flows seamlessly through ecosystems.
Energy Balance
Nature is all about balance. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration play a crucial role in maintaining the energy balance of our biosphere. While photosynthesis stores energy, cellular respiration releases it. This balance ensures that there’s always a steady supply of energy for all living organisms, from the tiniest bacteria to the largest whales.
FAQ
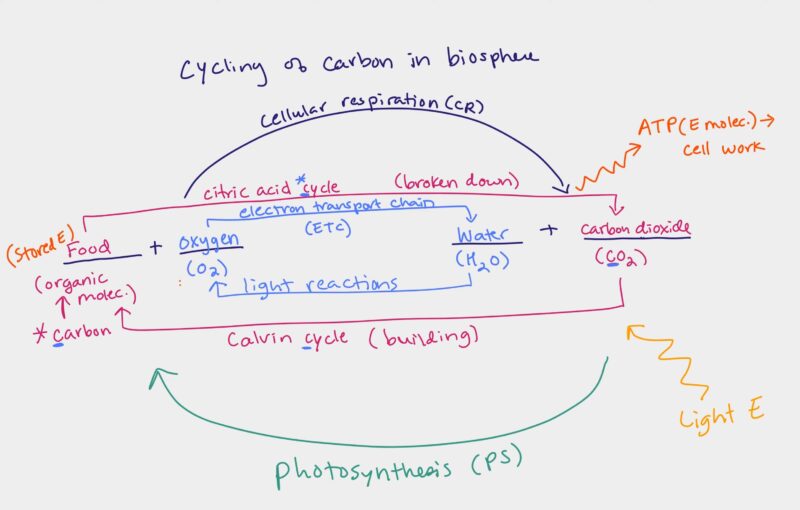
What is the importance of the carbon cycle in relation to photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
The carbon cycle is a vital ecological process where carbon is recycled in the biosphere. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration play pivotal roles in this cycle. While photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converts it into glucose, cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. This balance ensures that carbon is continuously cycled and reused, maintaining the health of our environment.
How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration contribute to maintaining stable atmospheric levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are like two sides of a coin. Photosynthesis takes in carbon dioxide and releases oxygen, while cellular respiration does the opposite. This exchange ensures that the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere remain stable, supporting life on Earth.
Do photosynthesis and cellular respiration occur simultaneously in plants?
Yes, plants carry out both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. While photosynthesis typically occurs during the day when sunlight is available, cellular respiration happens continuously, both day and night. This ensures that plants have a constant supply of energy to support their growth and other functions.
How is ATP involved in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
ATP, or Adenosine Triphosphate, is the primary energy currency of cells. In photosynthesis, the light-dependent reactions produce ATP, which is then used in the Calvin cycle to produce glucose. In cellular respiration, glucose is broken down to produce ATP, which cells use to power various functions.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration into the mesmerizing dance of photosynthesis and cellular respiration, it’s hard not to be in awe of nature’s genius. These two processes, though seemingly opposite, are intricately linked, ensuring the continuous flow of energy and life on our planet.
The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration is a testament to the interconnectedness of life. One cannot exist without the other. Plants capture the sun’s energy and convert it into food, while animals, including us, rely on this food for energy. And as we go about our daily activities, the carbon dioxide we release becomes the raw material for plants to start the cycle all over again.
So, the next time you take a deep breath or enjoy the shade of a tree, take a moment to appreciate the intricate ballet of nature that makes it all possible. It’s a dance of life, energy, and balance, and we’re all privileged to be a part of it.